ESP
Updated July 19, 2022 by luwol03, Shaquu and GogoVegaWhat is an ESP?
ESP is a microcontroller integrated circuit with Wi-Fi connection and very inexpensive. There are several versions of ESP, including ESP32, which is the latest version. ESP32 is more powerful and integrates Bluetooth connection. A popular option is Itead Sonoff modules which integrate an ESP, but the original firmware is not fully “open” so it cannot be easily added to systems like Node-RED. To solve this problem, ESP Easy or Tasmota firmware can be used to transform the ESP module into a simple multi-function sensor device for home automation solutions.
Why use an ESP with Node-RED?
Tasmota and ESP Easy integrate easily with many home automation solutions, usually over MQTT protocol. Node-RED has a full set of MQTT nodes, so using this hardware (or anything with MQTT) is simple and robust. There are various “MQTT standards” which may be compatible with Tasmota and ESP Easy including Domoticz, Homey, and HomeAssistant; these “standards” are MQTT topic and payload structures which are generally used to make discovery of devices easier.
Which ESP to choose?
Buy the one which does what you want! There are various choices:
- Plug-and-play modules (Itead Sonoff, Magic Home LED controllers, Shelly, and more)
- DIY hardware like ESP8285, ESP8266, ESP32, or similar with your own set of devices attached to the GPIO
Which firmware to choose for Flashing?
There are many firmware options, including simply writing your own using the Arduino IDE. We will focus on the two which seem most popular; they are similar in their operation. If you want to use a simple sensor, then Tasmota could be an easier starting point. If you want to create rules on-device (advanced use) then ESP Easy may be more robust.
Using in Node-RED
The use in Node-RED is done using the nodes MQTT in and MQTT out. If you don’t have an MQTT Server, you can install Aedes, which runs great inside Node-RED. You must then configure the address of the server (if using Aedes this will be localhost or the IP of your Node-RED instance) and the identifiers in the MQTT node as well as the Topic. The Topic is very important, it must match the topics your devices are using. We will discuss using Domoticz topics and the default Tasmota topics below.
Domoticz Topic
If your ESP device has Domoticz topics enabled, then the message will follow this format. The advantage of using Domoticz topics is having the standard format message, and is useful for those who are comfortable with the Domoticz topic structure. The identifier of your ESP will be idx in the message.
Topic : domoticz/in for MQTT in and domoticz/out for MQTT out node.
Example message at the output of the MQTT in node:
msg.payload = {
"idx": 1,
"nvalue": 0,
"svalue": '',
"RSSI": 10,
"Battery": 100
}
Read more about MQTT for Domoticz
Manual Topic
Topic or %topic% is the identifier (name) of your ESP, such as Light1, DeskLamp, GarageSensor, etc. depending on how you have named your devices. Messages using this topic structure will have a topic of %prefix%/%topic%/%event% where %prefix% is one of the 3 described below, %topic% is the identifier, and %event% is the event happening (could be POWER, SENSOR, TELE, or more depending on your device).
Tasmota uses 3 prefixes for forming a FullTopic:
cmnd - prefix to issue commands; ask for status
stat - reports back status or configuration message
tele - reports telemetry info at specified intervals
MQTT Nodes in Node-RED
Before starting, add an MQTT in node, then let’s go to the configuration:
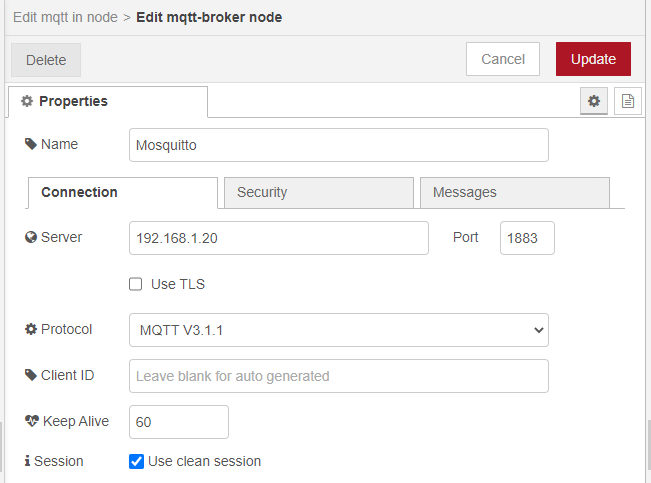
- MQTT Server
Put the IP address and port of your server.
User advance, you can choose the desired mqtt protocol.
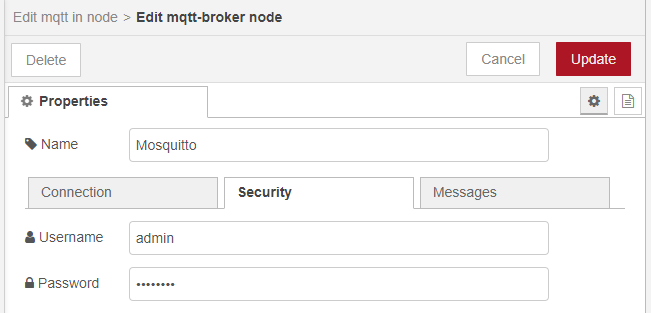
And put, if you have, the logins of your server.
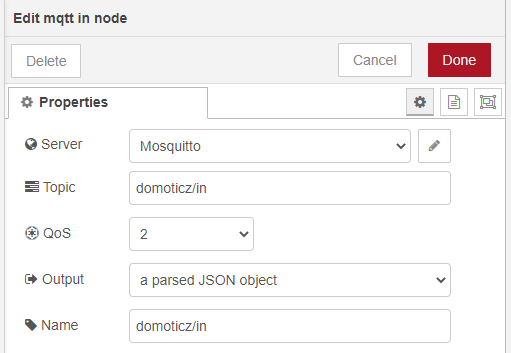
- MQTT Properties
Put the Topic as described above and select “A parsed JSON object” in Output.
Adding to NRCHKB
To connect the MQTT nodes to HomeKit, I offer you some examples for a Topic configuration with Domoticz and manual.
Here is a screenshot of the general structure of your flow:

Read more about Supported Peripherals by Tasmota
Domoticz Topic
- Doorbell
State to HK node:
if (msg.payload.idx == 1 && msg.payload.nvalue == 1) {
msg = {
"payload": {
"ProgrammableSwitchEvent": 0
}
}
return msg;
} else {
return;
}
- Fan/LightBulb/Outlet/Switch
State to HK node:
if (msg.payload.idx == 1) {
msg = {
"payload": {
"On": (msg.payload.nvalue) ? true : false
}
}
return msg;
} else {
return;
}
State to MQTT node:
msg = {
"payload": {
"idx": 1,
"nvalue": (msg.payload.On) ? 1 : 0
}
};
return msg;
- Humidity Sensor
State to HK node:
if (msg.payload.idx == 1) {
msg = {
"payload": {
"CurrentRelativeHumidity": msg.payload.nvalue
}
}
return msg;
} else {
return;
}
- Light Sensor
if (msg.payload.idx == 1) {
msg = {
"payload": {
"CurrentAmbientLightLevel": parseInt(msg.payload.svalue)
}
}
return msg;
} else {
return;
}
- Temperature Sensor
State to HK node:
if (msg.payload.idx == 1) {
msg = {
"payload": {
"CurrentTemperature": parseInt(msg.payload.svalue)
}
}
return msg;
} else {
return;
}
- Temperature + Humidity Sensor
State to HK node:
let Read = msg.payload.svalue.split(/\;/g);
msg1 = {
"payload": {
"CurrentTemperature": Read[0]
}
};
msg2 = {
"payload": {
"CurrentRelativeHumidity": Read[1]
}
};
if (msg.payload.idx == 1) {
return [msg1, msg2];
} else {
return;
}
Manual Topic
- Fan/LightBulb/Outlet
Topic in = stat/Light1/POWER
State to HK node:
let State;
if (msg.payload == "ON") {
State = true
} else if (msg.payload == "OFF") {
State = false
}
msg = {
"payload": {
"On": State
}
};
return msg;
Topic out = cmnd/Light1/POWER
State to MQTT node:
let State;
if (msg.payload.On) {
State = "ON"
} else {
State = "OFF"
}
msg = {
"payload": State
};
return msg;
- Humidity Sensor
Topic in = tele/Humidity/SENSOR
State to HK node:
msg = {
"payload": {
"CurrentRelativeHumidity": msg.payload.Humidity
}
};
return msg;
- Temperature Sensor
Topic in = tele/Temp/SENSOR
State to HK node:
msg = {
"payload": {
"CurrentTemperature": msg.payload.Temperature
}
};
return msg;
- Light Sensor
Topic in = tele/Light_Sensor/SENSOR
State to HK node:
msg = {
"payload": {
"CurrentAmbientLightLevel": msg.payload.Illuminance
}
};
return msg;